SWEATING.ie
Treatment of Excessive Sweating
General measures
Including antiperspirants, lifestyle changes and hypnosis.
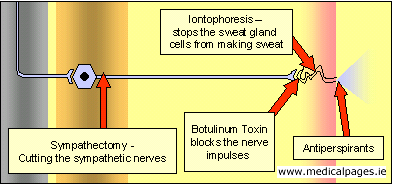
Iontophoresis
To control hand/foot sweating.

Botulinum injections
To stop armpit sweating
Surgery
ETS (Endoscopic Transthoracic Sympathectomy).
Excessive sweating usually occurs in specific areas of the body, however it can occur anywhere on the body. Some of the more common areas include:
- Armpit Sweating – also described as sweaty armpits,
- Hand Sweating – also described as sweaty hands, clammy hands, moist hand
- Feet Sweating – also described as sweaty feet, clammy feet, moist fee
- Facial Sweating – also described as sweaty face, blushing, facial blushing
Excessive Sweating
General measures can be taken to treat excessive sweating in some cases.
Changing behaviour
- Wearing lighter clothes
- Drinking less alcohol (but only if over drinking)
- Minimise rushing about
- Identifying when excess sweating occurs and – if only at certain times – minimise these situations/activities
Antiperspirants
Using the correct antiperspirant can make a significant difference for sweating. These can range from simple talcum powders that soak up mild sweat, through some of the spray-on antiperspirants to the very strongest Aluminium solutions that dry out the skin.
Aluminium Solutions are available without prescription from pharmacies. It is important that you read the instructions carefully before use. Aluminium antiperspirant solutions are called Anhydrol Forte and Driclor, and are identical.
Glycopyrralate
This is a drug that has what are termed ‘anti-cholinergic’ properties. It is available in impregnated tissue wipes that can be used to cleanse the skin.
Drug treatments
Unfortunately, there are no drugs that can be taken on a daily basis that will effectively stop sweating. A Beta Blocker such as Atenolol can sometimes be used for stressful events.
Counselling/Hypnotherapy
Sweating can become a viscious circle if it comes on due to stressful situations and you then worry about these situations occurring. Counselling or hypnotherapy can be very useful for some people in overcoming this as they can be taught to control a stressful situation
Iontophoresis can effectively treat hand and feet sweating by applying a low intensity electrical current to the hands or feet by means of an iontophoresis machine containing ordinary tap water. The electric current and mineral particles in the water act together to microscopically thicken the outer layer of the skin, thereby blocking the flow of sweat to the skin’s surface. Once this sweat output is blocked or interrupted, sweat production in the treated areas stops. Iontophoresis has been proven to be effective in up to 98.5% of people.

Most people with hyperhidrosis will experience complete cessation of sweating after the initial phase of treatment; this sweat free period can last from a few days to a month or so, depending on the individual. After the initial intensive treatment phase the dryness can be kept under control by regular maintenance treatments. The frequency of maintenance treatments varies from person to person and varies from twice weekly to monthly.
This is the treatment of choice for hand and foot sweating.
Iontophoresis does not ‘cure’ sweating but it does control it. Continuous use will ensure that your hands and feet are kept dry. This should be at least once a fortnight, or even once a week for 30 minutes.
For this reason it is impractical to keep attending a clinic or hospital, and is why most sufferers buy a machine for home use.
The most effective way to treat armpit sweating – Axillary hyperhidrosis – is by injecting a dilute solution of Botulinum into the skin of the armpit. A very fine needle is used so that the procedure almost painless.
- Approximately 12 to 16 injections are made in each armpit
- No anaesthetic is needed
- the whole process takes only 20 minute
- Both armpits are injected in the same session
- Botulinum takes a few days to work
- Because there are no muscles in the armpit, there is no real risk of loss of muscle power, a possible problem with Botulinum elsewhere
- Botulinum binds to the nerves that control sweating
- Sweating can be reduced by 90% times
- A first course usually lasts 4 – 9 months, with subsequent courses being more effective and lasting 6 – 12 months per time
Botulinum Toxin is a very specific natural poison that causes Botulinism. Advances in the pharmaceutical industry have allowed very pure Botulinum Toxin to be manufactured and minute doses to be accurately measured and distributed for medical use. These doses are large enough to have a local effect where injected, but are far too small to have any effect on our breathing or movement.
When a nerve meets whatever it is that it needs to communicate with, the junction between the two is called a “synapse”. The synapse where the sympathetic nerves meet the sweat glands can be blocked by Botulinum. As the sweat glands are in the skin itself, injection of a solution of Botulinum into the skin causes a blocking of the impulses from the sympathetic nervous system and so sweating will stop.
Does Botulinum hurt when injected? Only minimally. Because the skin of the armpit is thin, injections there are barely felt. The needles used are extremely fine, and they themselves are not felt. The Botulinum itself stings a little.
Does Botulinum stop all the armpit sweating? No, not all of it, usually about 90%. This more than four-fold decrease means that hyperhidrosis sufferers, after Botulinum, sweat far less than the average person.
Is Botulinum safe? In the armpit, yes. There are no muscles there that it could affect. In other areas, for example, the hands or face, it could temporarily weaken the muscles if injected into the wrong place.
Is Botulinum expensive? No, not when you consider the cost of frequent changes of clothing, deodorants etc. The cost of embarrassment and social phobia is also high. For therapeutic use, the cost is claimable against tax with the government MED1 scheme.
Who should not have Botulinum?
There are few contraindications, the main ones being pregnancy and some very rare neurological illnesses. These will be discussed at your appointment.
How can I arrange ETS?
ETS is performed by consultant vascular surgeons. You can discuss referral with your own GP. As with all surgical procedures there are side effects and complications that patients and their relatives must be aware of before going through with this operation.
Risks of Endoscopic Transthoracic Sympathectomy
1 – Compensatory Hyperhidrosis
The body needs to cool itself so, if the arms and head are treated by ETS, the sweat that should have come from these areas is re-distributed elsewhere. This re-distribution of sweating is called Compensatory Hyperhidrosis. It can be especially noticeable in the small of the back – and some people find this unbearable.
2 – Damage to the Lung needing a chest drain
Rarely, in approximately 1 in 100 patients, the lung can be damaged during the surgery, leading to a tube called a “chest drain” having to be put in place for a couple of days to make sure that the lung re-inflates. Even more rarely, the lung needs to be repaired after such an injury.
3 – Horner’s Syndrome
If too much of the chain is damaged, the face can become dry on the same side, the eye lid can droop a little and the eye itself can have a dilated pupil (Horner’s syndrome).
4 – Winging of the Scapula
There have been reports that the nerve to the muscle of the shoulder blade can be damaged leading to “winging” of the shoulder blade. This means that the shoulder blade moves out to the side and needs intensive physiotherapy to see if it can be brought back again.
5 – Injury to a major structure in the Chest
The chest houses some of the largest and most important structures in the body – particularly the Heart, the Great Blood Vessels and the Lungs. Knowing this, surgeons are always exceptionally careful when doing an ETS. However, there is always a very small chance that one of these structures can be damaged. One final thing of importance – ETS is a permanent procedure – it cannot be reversed if the patient changes their mind.


